 In my previous blog, I discussed digitization in the public sector, why that is happening and the benefits of this massive transformation. I introduced the technologies which are enabling digitization; cloud, software-defined networks, analytics, and IoT, but did not dive into how those technologies are deployed. As part of any modernization effort, all four of these technologies must be researched and understood before any plan is initiated. So for the next several posts, I am going to go into more detail on these technologies behind digitization. Let’s start with the Wide Area Network (WAN).
In my previous blog, I discussed digitization in the public sector, why that is happening and the benefits of this massive transformation. I introduced the technologies which are enabling digitization; cloud, software-defined networks, analytics, and IoT, but did not dive into how those technologies are deployed. As part of any modernization effort, all four of these technologies must be researched and understood before any plan is initiated. So for the next several posts, I am going to go into more detail on these technologies behind digitization. Let’s start with the Wide Area Network (WAN).
Why the WAN?
The WAN is often taken for granted and yet it is one of the most critical elements of any CIO’s portfolio. It is considered a mature component, meaning it’s stable and not seen as a unique differentiation for IT. The WAN delivers the connectivity between all resources and, from the end user perspective, as long as it works no one even thinks about it.
Over the last 20 years, the architecture for the WAN has been refined to provide more bandwidth and support the internet impact on the network, but for the most part it is the same design framework. However, with the proliferation of metro Ethernet, adoption of the cloud and the IoT, it is now time to modernize the WAN! Cisco sees 55 percent of organizations across industries looking to modernize their WAN in the next year. So what kind of WAN should public sector organizations be aiming for?
Current WAN Model
The current WAN architecture (hub and spoke) was designed to bring all traffic from remote users and the branch offices back to the headquarters where the data center was typically located. This made sense as all the applications were based in the data center, and centralizing security technologies could provide a controlled environment. Since 2010, many CIOs both in and outside of public sector have been moving many of their workloads and applications to the Public Cloud. Gartner foresees double-digit growth in government use of public cloud services, with spending forecast to grow on average 17.1% per year through 2021. With that migration, this legacy model makes less sense, especially as the applications are no longer in the agency data center. Now all the traffic is still going to the security systems in the data center, but it must also loop back out of the data center and go to the public cloud where the applications reside. This ‘hair-pinning’ effect adds latency for the users, increases costs for security components that need to scale to support the traffic flows, and increases complexity.
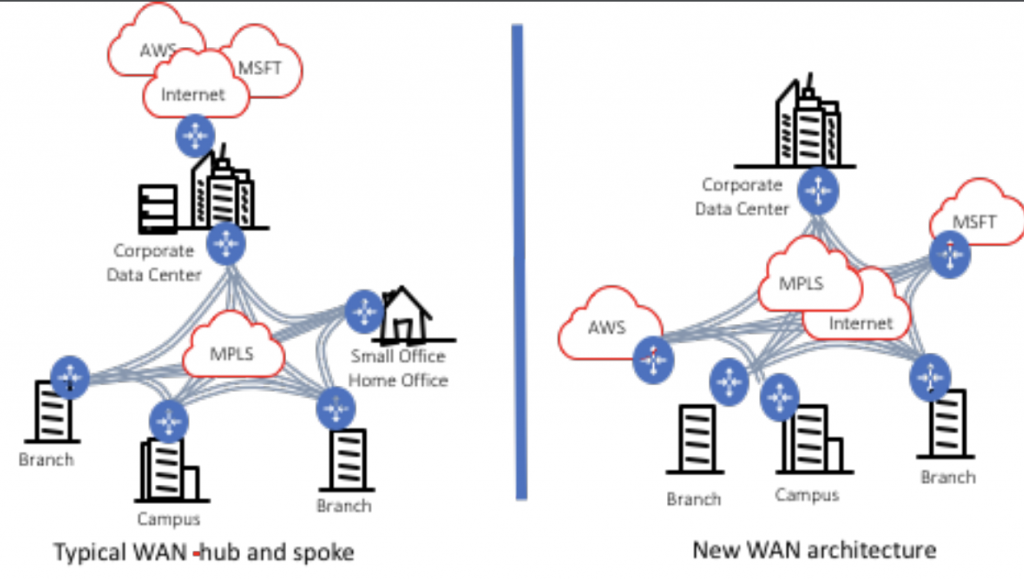
A New WAN Model
To address this new application delivery paradigm and the increased value of the internet as a transport, a new WAN model is gaining popularity. That model is called Software-Defined WAN, or SD-WAN. It is based on the premise that the internet is a viable transport, leveraging encryption technologies. By using the Internet as a transport this allows users direct access to the application or resources in the public cloud, without going back to the data center. Thus providing a lower cost WAN model with a better user experience. This model can coexist with the MPLS networks and bandwidth can be optimized based on the user traffic. SD_WAN which is software defined, allows for simplified configuration management, zero touch provisioning, and on demand changes to the system.
This new model provides some key benefits:
- Major cost reduction relating to WAN, including circuit cost, operational expenditure, and the ability to leverage lower-cost bandwidth services.
- Simplified deployment and installation capabilities through optimized zero-touch provisioning for remote locations, centralized deployment of policy and management.
- Intelligent traffic steering based on application awareness of the application’s locations (on-premise, public cloud like Amazon Web Services (AWS) and Azure, or SaaS) and SLA requirements needed over a specific WAN link, including application brownout mitigation.
- Provide secure, zero-trust, authenticated transport, topology-driven network-wide segmentation (L3 VPN segmentation), and the ability to offer insertion of security services into the traffic flow, including firewalls, IDS, and third-party solutions.
- Advanced analytics for both real-time insight to the WAN fabric’s behavior, as well as future-looking “what-if” analysis for billing and capacity planning, all managed from the cloud.
With new technologies like cloud and IoT, as well as the operational use of the internet, public sector organizations should consider a more modern WAN solution. SD-WAN will provide secure use of the internet as a transport, lower the operational costs of WAN management and allow IT to more quickly respond to business needs.
Dan Kent is part of the GovLoop Featured Contributor program, where we feature articles by government voices from all across the country (and world!). To see more Featured Contributor posts, click here.





Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.